Sterilization Technologies in Medical Devices: Pros, Cons & Trends


Sterilization is one of the most critical steps in the medical device manufacturing process. With rising global demand, stricter regulations, and concerns about patient safety, choosing the right sterilization technique has become a strategic decision for device manufacturers.
This blog explores the most widely used sterilization technologies, their advantages and limitations, and the emerging trends shaping the future of medical device sterilization.
🔬 1. Why Sterilization Matters in Medical Devices
Medical devices—especially those that are invasive, implantable, or come into contact with bodily fluids—must meet strict bioburden and sterility assurance level (SAL) requirements.
Sterilization ensures:
elimination of microorganisms
compliance with FDA, CE, and ISO 11135/11137
extended shelf-life
patient safety and reduced infection risks
⚙️ 2. Major Sterilization Technologies in Medical Devices
2.1 Ethylene Oxide (EtO) Sterilization


How it works:
Uses ethylene oxide gas at low temperature to sterilize heat/moisture-sensitive devices.
✔ Pros:
Ideal for plastics, polymers, electronics, and complex lumens
Penetrates deep into packaging and device cavities
Works at low temperatures → protects delicate materials
High compatibility across device categories
✖ Cons:
Long cycle time (aeration required)
Environmental and worker safety concerns
Increasing regulatory scrutiny (US EPA tightening guidelines)
Best for:
Catheters, wound dressings, syringes, tubing, electronic medical devices.
2.2 Gamma Radiation Sterilization


How it works:
Uses Cobalt-60 gamma rays to destroy microorganisms.
✔ Pros:
Highly reliable & widely used
Faster cycle time vs EtO
Good penetration power
Suitable for bulk processing
✖ Cons:
May degrade certain polymers (e.g., polypropylene)
Requires dedicated, high-cost irradiation facilities
Radioactive material handling challenges
Best for:
Surgical gloves, syringes, IV sets, implants, single-use disposables.
2.3 Electron Beam (E-Beam) Sterilization

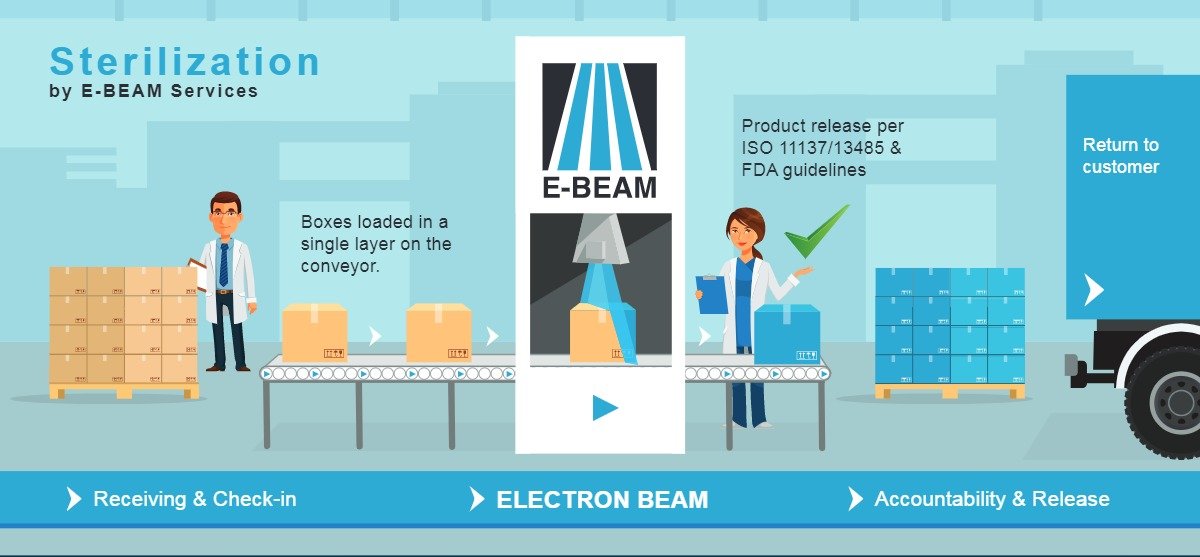
How it works:
High-energy electrons sterilize the device surface.
✔ Pros:
Very rapid cycle (< minutes)
No radioactive source used
Suitable for high-volume throughput
Better for thinner materials
✖ Cons:
Limited penetration compared to gamma
Not ideal for densely packaged products
Higher upfront equipment cost
Best for:
Surgical supplies, syringes, drug–device combination products.
2.4 Steam Sterilization (Autoclaving)


How it works:
High-pressure saturated steam (121–134°C).
✔ Pros:
Most cost-effective method
Fast and environmentally friendly
No toxic residues
✖ Cons:
Not suitable for moisture- or heat-sensitive devices
May damage adhesives, electronics, polymers
Best for:
Metal instruments, surgical tools, reusable devices.
2.5 Plasma (Hydrogen Peroxide) Sterilization


How it works:
Uses vaporized hydrogen peroxide + plasma to sterilize at low temperature.
✔ Pros:
Low-temperature, safe, and residue-free
Faster than EtO
Eco-friendly
✖ Cons:
Limited penetration in long lumens
Packaging compatibility issues
Not suitable for cellulose-based materials
Best for:
Endoscopes, cameras, sensitive electronics.
📊 3. Sterilization Technology Comparison Table
| Method | Temperature | Penetration | Material Compatibility | Cycle Time | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EtO | Low | Excellent | Very High | Long | Medium |
| Gamma | Low | Excellent | High | Medium | High |
| E-Beam | Low | Moderate | Moderate | Very Fast | High |
| Steam | High | Good | Low | Fast | Low |
| Plasma | Low | Moderate | Moderate | Fast | Medium |
🌍 4. Emerging Trends in Medical Device Sterilization


🔹 Trend 1: Shift Away from Ethylene Oxide (Regulatory Pressure)
Global regulatory bodies (EPA, FDA) are tightening EtO emissions standards.
Companies are exploring alternatives like VHP, e-beam, and X-ray.
🔹 Trend 2: Rise of X-Ray Sterilization
X-ray sterilization combines the penetration of gamma with the flexibility of e-beam.
Why it’s growing:
No radioactive material needed
Better supply chain stability
Works for thicker materials
🔹 Trend 3: Sustainability & Green Sterilization
Manufacturers are reducing reliance on ethylene oxide, improving aeration systems, and adopting renewable-energy-powered irradiation.
🔹 Trend 4: Single-Use Devices (SUDs) Driving Volume
The rise of disposables → higher demand for large-scale sterilization facilities.
🔹 Trend 5: Integration of IoT & Automation in Sterilization Facilities
Real-time monitoring, automated cycle validation, and AI-driven quality control are transforming the sterilization workflow.
🔍 5. How to Choose the Right Sterilization Method
Consider these factors:
Material compatibility
Device design (lumens, electronics, coatings)
Regulatory pathway
Throughput requirement
Environmental impact
Cost efficiency
Many companies use multiple sterilization methods depending on product family.
🏁 Conclusion
Sterilization technology is evolving faster than ever, shaped by regulatory pressure, sustainability goals, and technological innovation.
For medical device manufacturers, choosing the right sterilization method is not just a compliance requirement—it’s a strategic decision that impacts product safety, cost, and brand reputation.